SEO stands for Search Engine Optimisation. It’s all about making your website easy to find when people search for things online. Especially, it’s crucial for businesses looking to improve their online visibility and attract qualified website traffic. In this, SEO for beginners guide we will teach you the fundamentals of SEO and how to leverage it for maximum impact.
Ready to get your website noticed on Google? At UTDS Optimal Choice, we simplify SEO, helping small businesses boost their online visibility. Whether you’re just starting or looking to refine your strategy, our expert team can guide you every step of the way. Get in touch today to start improving your search rankings and drive more traffic to your site!
What Is SEO?

Imagine you have a lemonade stand. SEO is like putting up big, colourful signs that help people find your stand. But instead of physical signs, SEO uses special techniques to make your website stand out on the internet.
Here’s how it works:
- When you search for something online, you use a search engine like Google.
- Google looks through millions of websites to find the best matches for what you’re looking for.
- It then shows you a list of these websites, ranked from most helpful to least helpful.
SEO helps your website become one of those top helpful results. It’s like telling Google, “Hey, my website has great information about this topic!“
To do this, SEO uses things like:
- Using the right words that people are searching for
- Making your website easy to use and understand
- Getting other trusted websites to link to yours
Most importantly, remember SEO isn’t about tricking search engines. It’s about making your website/content truly useful for the audience and making sure search engines understand that. It’s one of the important factors to rank in Google search. Here is a detailed guide by Lily Ray about Google’s helpful content update and ranking system to give you a better clarity into why useful content matters the most in SEO.
Why Should You Care About SEO?
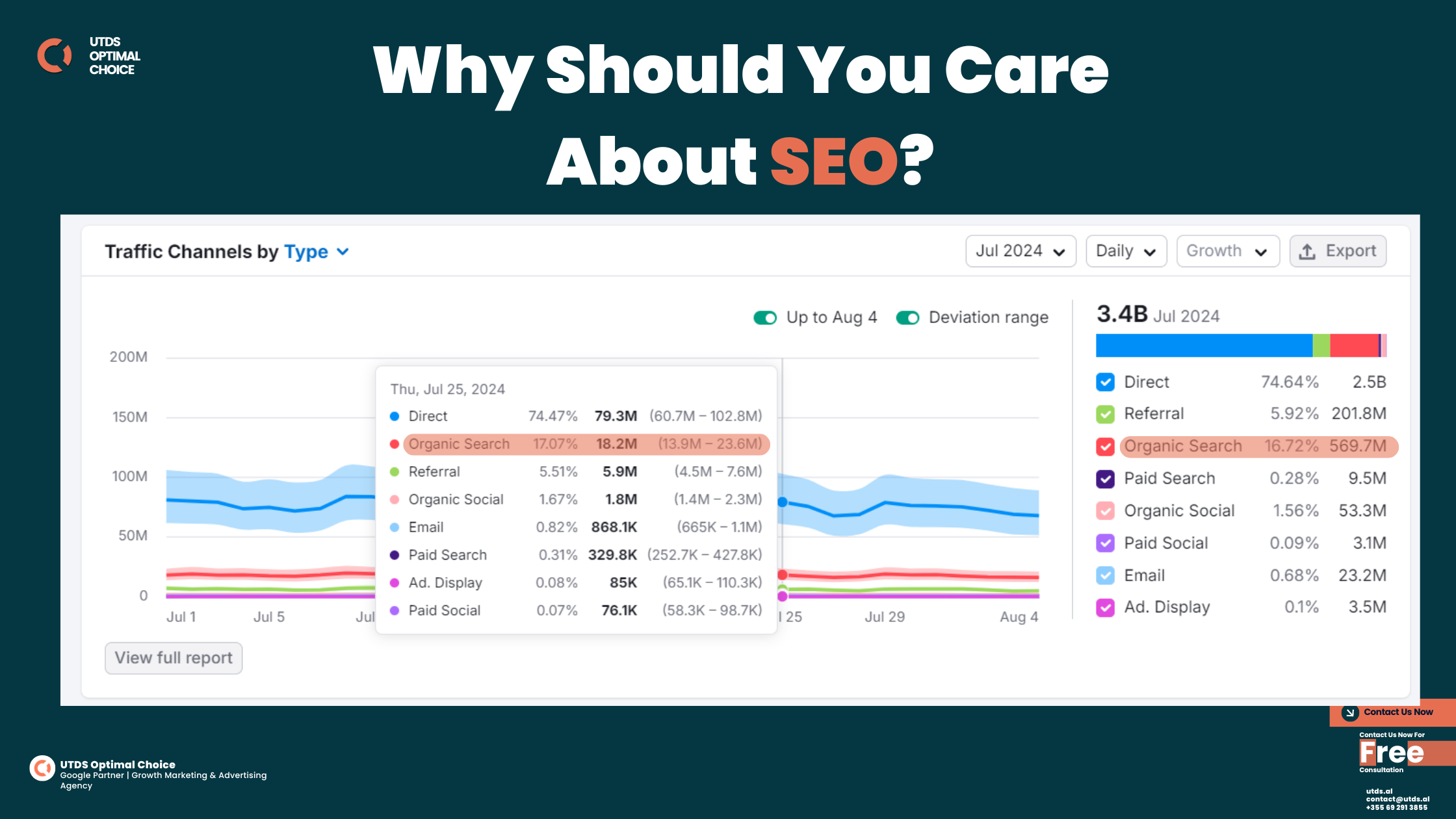
SEO is super important if you have a website, whether it’s for a business, a blog, or anything else. Here’s why:
- More visitors: Good SEO helps more people find your website. It’s like having a shop on a busy street instead of a quiet alley.
- Trust: When your website shows up at the top of search results, people trust it more. They think, “If Google says this is good, it must be!“
- It’s free (mostly): Unlike paying for ads, the visitors you get from SEO don’t cost you money each time someone clicks.
- Long-lasting results: SEO can take time to work, but once it does, the benefits can last for a long time.
- Better user experience: Many things that are good for SEO also make your website better for visitors.
- Stay ahead of competitors: If you’re not doing SEO, but your competitors are, they might get all the visitors instead of you.
SEO is not a one-time thing. It’s ongoing work to keep your website helpful and visible. It’s one of the common misconception, but Do you know? Google frequently updates their Google Search Algorithm which always require new strategies in order to rank in SERPs. Want to have a small peak into ranking factors exposed by Google Algorithm Leak? Check here
SEO For Beginners
Types Of SEO
There are three main types of SEO. Think of them as different parts of a healthy meal – you need all of them to get the best results!
- On Page SEO: This is all about making each page on your website as good as it can be. It includes:
- Using the right keywords (important words people search for)
- Writing clear, helpful content
- Using good titles and descriptions for your pages
- Off-Page SEO: This is about improving how other websites see yours. The main part of this is getting other sites to link to yours. Off-Page SEO includes:
- Building relationships with other websites
- Creating content that people want to share
- Being active on social media
- Technical SEO: This is the behind-the-scenes work that makes your website run smoothly. Technical SEO includes:
- Making your website load quickly
- Making sure website works well on mobile phones
- Helping search engines understand your site structure
As you learn more about SEO, you’ll discover how these three types work together to improve your website’s visibility in search results.
Common SEO Terms
Here’s a simple guide to some words you’ll often hear when learning about SEO:
- Keywords: The words and phrases people type into search engines. You want your website to use these words.
- Meta tags: Hidden descriptions of your web pages that help search engines understand what they’re about.
- Backlinks: Links from other websites to yours. They’re like votes of confidence for your site.
- SERP: Stands for “Search Engine Results Page.” It’s the list of websites you see after you search for something.
- Organic traffic: Visitors who come to your site by clicking on a non-paid search result.
- Crawling: When search engines look through your website to understand what it’s about.
- Indexing: When search engines add your web pages to their list of sites to show in search results.
- Alt text: Descriptions of images on your website. They help search engines understand your pictures.
Don’t worry if these seem confusing at first. As you learn more about SEO, they’ll become clearer!
Feeling overwhelmed by SEO jargon? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. At UTDS Optimal Choice, we break down complex SEO terms into simple, actionable strategies that help you get found online. Whether you need help with keyword research or improving your site's performance, our team is here to assist. Contact us today to learn how we can boost your website's search rankings and make SEO work for you
How Search Engines Work
Basics of Search Engine Algorithms
When you type something into a search engine like Google, it seems like magic how quickly you get results. But there’s no magic wand – just clever computer programs called Google algorithms. Let’s break down how these algorithms work:
- Understanding Your Question: The algorithm first tries to understand what you’re asking. It looks at;
- The words you use
- The order of the words
- Any spelling mistakes
- Finding Relevant Pages: Then, it looks through billions of web pages to find ones that match your question. It’s like a librarian finding books on a topic.
- Checking Page Quality: Not all web pages are equal. The algorithm checks how good each page is by looking at;
- How many other websites link to this page (this is called “authority“)
- How well-written and clear the content is
- If the website is safe and trustworthy
- Looking at User Experience: The algorithm also cares about how easy the website is to use;
- Does it load quickly?
- Is it easy to read on a phone?
- Do people usually find what they need on this site?
- Personalisation Search engines: Try to give you results that fit you best. They might consider;
- Where you are (to show nearby places)
- What language you speak
- What you’ve searched for before
- Freshness: For some topics, newer information is better. The algorithm checks how recent the information is.
- Putting It All Together: Finally, the algorithm uses all this information to rank the pages. The best matches appear first in your search results.
Search engines are always updating their algorithms to give better results. They want to make sure you find exactly what you’re looking for, as quickly as possible.
Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking: How Search Engines Find and Organise Information
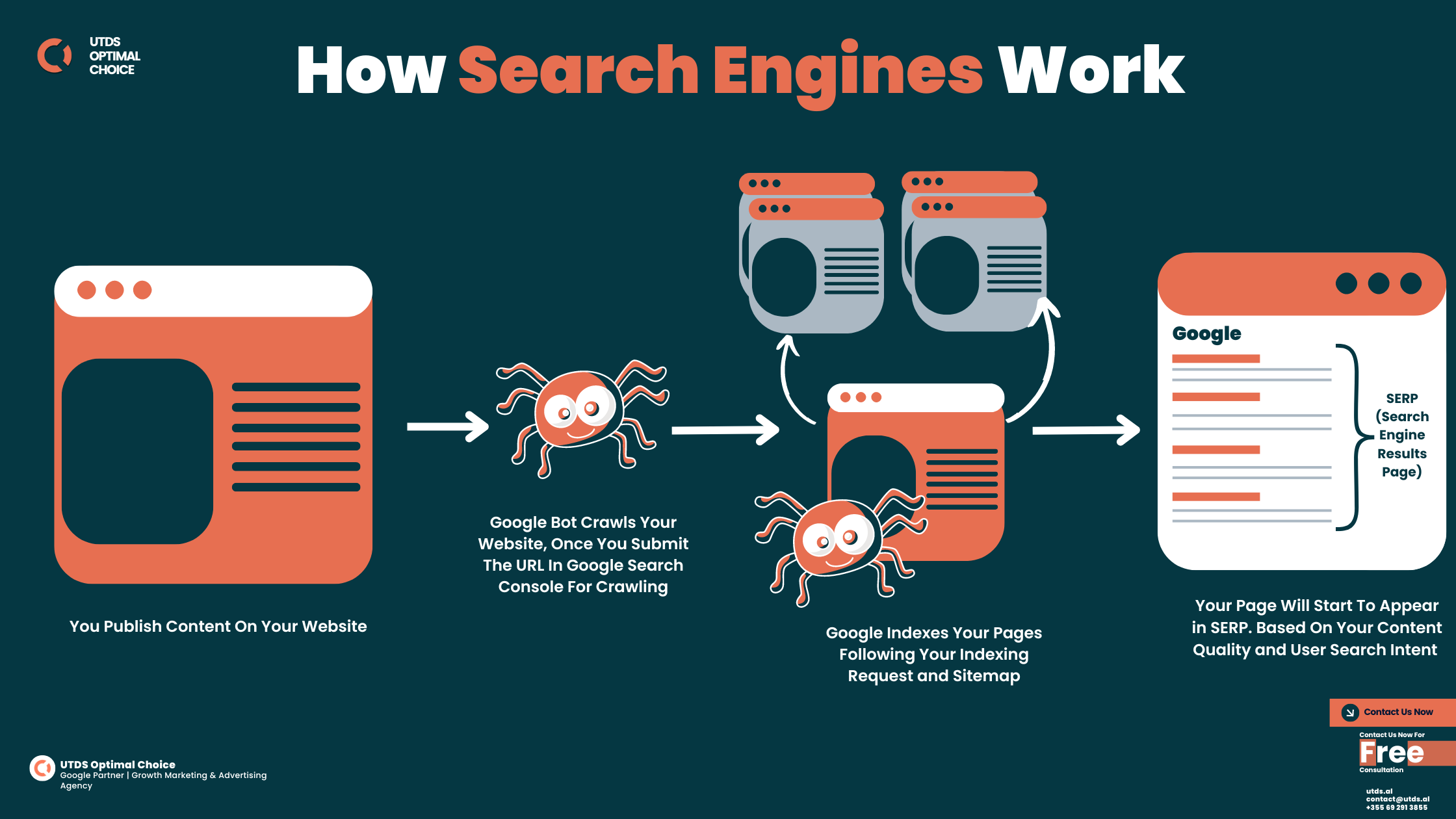
Search engines work kind of like very fast and very smart. They go through three main steps to get you the information you need:
- Crawling: Finding the Pages/Content
- Imagine tiny robots (called “crawlers” or “spiders“) that zoom around the internet.
- These crawlers visit websites, jumping from link to link, just like you might click around on the internet.
- They look at the words, pictures, videos, and other content on each page they visit.
- It’s like the librarian walking through a giant library, looking at every book.
- Indexing: Organising the Information
- After the crawlers find a page, the search engine tries to understand what it’s about.
- It looks at things like:
- The words on the page
- The titles and headings
- The links to and from the page
- The type of content (text, images, videos)
- Then, it stores this information in a huge database called an index.
- This is like the librarian writing down information about each book on index cards and organising them.
- [Here is the complete overview of Google Developers crawling and indexing guide]
- Ranking: Deciding What’s Most Helpful
- When you search for something, the search engine looks through its index.
- It pulls out all the pages that might answer your question.
- Then, it decides which ones are most likely to be helpful to you.
- This is where those algorithms we talked about earlier come in.
- They look at hundreds of factors to decide which pages to show you and in what order.
- It’s like the librarian deciding which books to recommend based on what they know about the books and about you.
This whole process happens in just a fraction of a second! Every time you search, the search engine does all this work to try to give you the best possible answer.
It’s also important to know that search engines are always updating their index. They regularly re-crawl websites to find new information and keep their results up-to-date.
Understanding SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages)
When you search for something online, the page you see with all the results is called a SERP – Search Engine Results Page. Let’s explore what you’ll find on a SERP:
Organic Results
- These are the main search results, ranked by the search engine’s algorithm.
- They’re called “organic” because no one paid for them to be there.
- Usually, these make up most of the results you see.
Paid Ads
- These are results that companies have paid to show up for certain searches.
- They’re usually marked with a small “Ad” label.
- They often appear at the top or bottom of the page.
- Sometimes, Google shows a box at the top with a direct answer to your question.
- This could be a paragraph, a list, or even a table.
- It’s meant to give you a quick answer without needing to click on a website.
Local Pack
- If you search for something that could be nearby (like “pizza“), you might see a map with local businesses.
- This usually includes addresses and phone numbers.
Image Results
- For some searches, you’ll see a row of images.
- Clicking these takes you to Google Images with more picture results.
Video Results
- Similar to images, sometimes you’ll see video thumbnails in the results.
News Results
- For current topics, you might see a box with recent news articles.
People Also Ask
- This is a box with related questions. Clicking on a question expands it to show the answer.
Knowledge Panel
- For some searches (like famous people or places), you might see a box on the right with key information.
Shopping Results
- If you search for a product, you might see pictures, prices, and places to buy it.
SERPs can look different depending on what you search for, where you are, what device you’re using, and most importantly search intent.
On Page SEO
Keyword Research
Keyword research is the foundation of good SEO. It’s about finding the words and phrases people use when they search for content like yours. Here’s how to do it effectively:
Brainstorm Seed Keywords
- Start by listing topics related to your business or content.
- Think about what your target audience might search for.
- Example: If you sell running shoes, seed keywords might include “running shoes,” “jogging footwear,” “marathon shoes.”
- Google Keyword Planner (free with Google Ads account):
- Enter your seed keywords.
- Look at the “Keyword ideas” tab.
- Pay attention to average monthly searches and competition.
- Ahrefs Keyword Explorer:
- Enter a seed keyword.
- Check the “Phrase match” report for related keywords.
- Look at “Keyword Difficulty” and “Search Volume.”
- SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool:
- Type in your main keyword.
- Use filters to sort by volume, difficulty, or user intent.
- Look at the “Questions” tab for related queries.
- Google Keyword Planner (free with Google Ads account):
Analyse the Results
- Look for keywords with:
- Decent search volume (depends on your niche, but generally 100+ monthly searches)
- Manageable competition (lower difficulty scores are easier to rank for)
- Relevance to your content or products
- Look for keywords with:
Consider Search Intent
- Informational Intent: People looking for information (e.g., “how to choose running shoes“)
- Navigational: Searching for a specific website (e.g., “Nike running shoes“)
- Commercial: Researching before buying (e.g., “best running shoes for marathons“)
- Transactional Intent: Ready to buy (e.g., “buy Brooks Ghost 14 running shoes“)
Look for Long-Tail Keywords
- These are longer, more specific phrases.
- They often have less competition and more focused intent.
- Example: “breathable running shoes for summer marathons“
- Use tools to see what keywords your competitors rank for.
- Look for gaps – keywords they’re missing that you could target.
Create a Keyword List
- Organise your findings into a spreadsheet.
- Include columns for keyword, search volume, difficulty, and keyword search intent.
- Prioritise keywords based on your goals and resources.
Keyword research isn’t a one-time task. Keep updating your list as trends change and you create new content. Use these keywords to guide your content creation and on-page optimisation efforts.
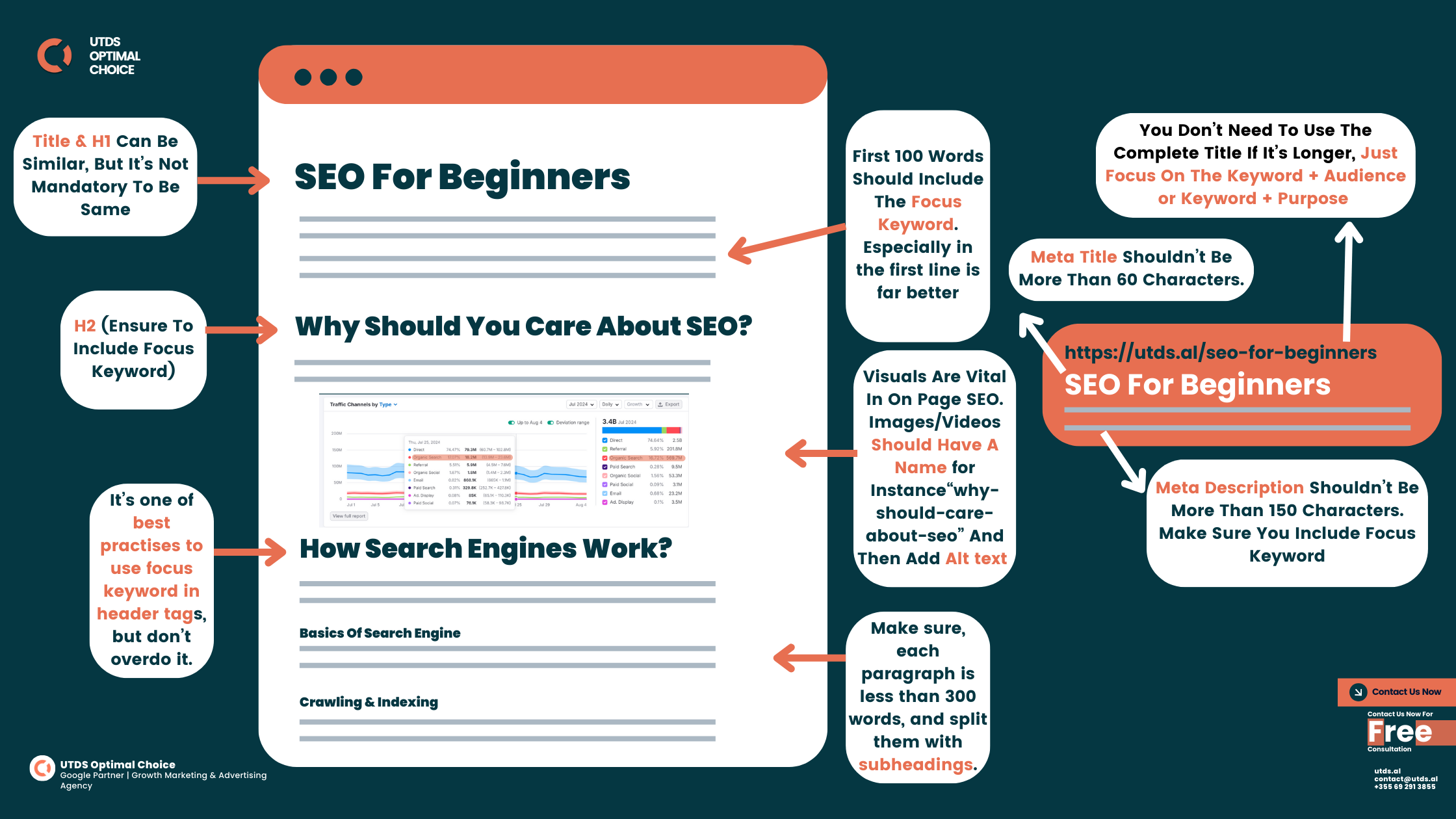
Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Title tags and meta descriptions are part of meta tags and crucial for SEO. They’re often the first thing users see in search results, so they need to be compelling and informative. Here’s how to optimise them:
Title Tags
- What are Title Tags?
- They’re the main text you see in search results.
- They also appear at the top of your browser when you visit a page.
- HTML format: <title>Your Title Here</title>
Best Practices for Title Tags:
- Length: Keep it under 60 characters to avoid truncation in search results.
- Include your main keyword: Put it as close to the beginning as possible.
- Be descriptive: Clearly explain what the page is about.
- Include your brand name: Typically at the end, separated by a pipe (|) or dash (-).
- Be unique: Each page should have a different title tag.
- Use natural language: Write for humans, not just search engines.
- Examples of Good Title Tags:
- Product page: “Brooks Ghost 14 Running Shoes | SuperSports”
- Blog post: “10 Tips for Choosing the Right Running Shoes – RunExpert”
- Category page: “Men’s Running Shoes: Top Brands & Styles | MegaRun”
Meta Descriptions
- What are Meta Descriptions?
- The short text below the title in search results.
- They don’t directly impact rankings but affect click-through rates.
- HTML format: <meta name=”description” content=”Your description here”>
- Best Practices for Meta Descriptions:
- Length: Aim for 150-160 characters to avoid truncation.
- Include keywords: Use your main keyword and related terms naturally.
- Write a compelling copy: Encourage users to click through to your site.
- Include a call-to-action: Tell users what they’ll get by clicking.
- Match search intent: Align with what users are looking for.
- Be unique: Like title tags, each page should have a different meta description.
- Examples of Good Meta Descriptions:
- Product page: “Experience cloud-like comfort with the Brooks Ghost 14 running shoes. Featuring DNA LOFT cushioning and a segmented crash pad for smooth transitions. Shop now!”
- Blog post: “Confused about choosing running shoes? Our expert guide breaks down 10 essential factors to consider, from arch support to cushioning. Find your perfect fit!”
- Category page: “Explore our wide range of men’s running shoes from top brands like Nike, Adidas, and Brooks. Whether you’re a beginner or marathon runner, find your ideal pair today.”
While search engines may sometimes generate their own meta descriptions, providing well-crafted meta descriptions gives you more control over how your pages appear in search results. Regularly review and update your title tags and meta descriptions to improve your click-through rates and overall SEO performance.
Content Optimisation
Creating content that both search engines and users love is key to successful SEO. Here’s how to optimise your content effectively:
Use Your Target Keyword Wisely
- Include your main keyword in:
- The first 100-150 words of your content
- At least one subheading (H2 or H3 tag)
- The conclusion
- Don’t overdo it! Aim for a keyword density of about 1-2%
- Include your main keyword in:
Optimise for Related Keywords
- Use synonyms and related terms naturally throughout your content
- This helps with semantic SEO, showing search engines your content is comprehensive
- Example: If your main keyword is “running shoes,” use related terms like “jogging footwear,” “athletic shoes,” “trainers“
Create High-Quality, In-Depth Content
- Aim for comprehensive coverage of your topic
- Longer content often ranks better (aim for at least 1000 words for most topics)
- But quality trumps quantity – every word should add value
Structure Your Content for Readability
- Use short paragraphs (2-3 sentences each)
- Include plenty of subheadings (H2, H3, H4) to break up text
- Use bullet points and numbered lists for easy scanning
- Include relevant images, videos, or infographics
Optimise Your URL
- Keep it short and descriptive
- Include your main keyword
- Use hyphens to separate words
- Example: yoursite.com/best-running-shoes-for-beginners
Use Proper Heading Structure
- Use only one H1 tag per page (usually your main title)
- Use H2s for main sections, H3s for subsections, etc.
- Include keywords in your headings naturally
Optimise Images
- Use descriptive file names (e.g., “brooks-ghost-14-running-shoes.jpg“)
- Include alt text with keywords (e.g., “Brooks Ghost 14 blue running shoes“)
- Compress images to improve page load speed
Include External and Internal Links
- Link to high-quality, relevant external sources
- Include internal links to your own related content
- Use descriptive anchor text for links
- Make sure your content matches what users are looking for
- Address common questions related to your topic
- Provide actionable information or clear next steps
Keep Content Fresh
- Regularly update your content with new information
- Add new sections or examples to expand on your topic
- Remove or update any outdated information
Improve Readability
- Use simple language (aim for a grade 6-8 reading level)
- Break up long sentences
- Define technical terms if your audience might not be familiar with them
- Include a clear, concise answer to a common question near the top of your content
- Use structured data markup when appropriate
While these tactics are important for SEO, always prioritise creating valuable, engaging content for your human readers. Search engines are getting better at recognising high quality content that truly serves user needs.
Internal Linking
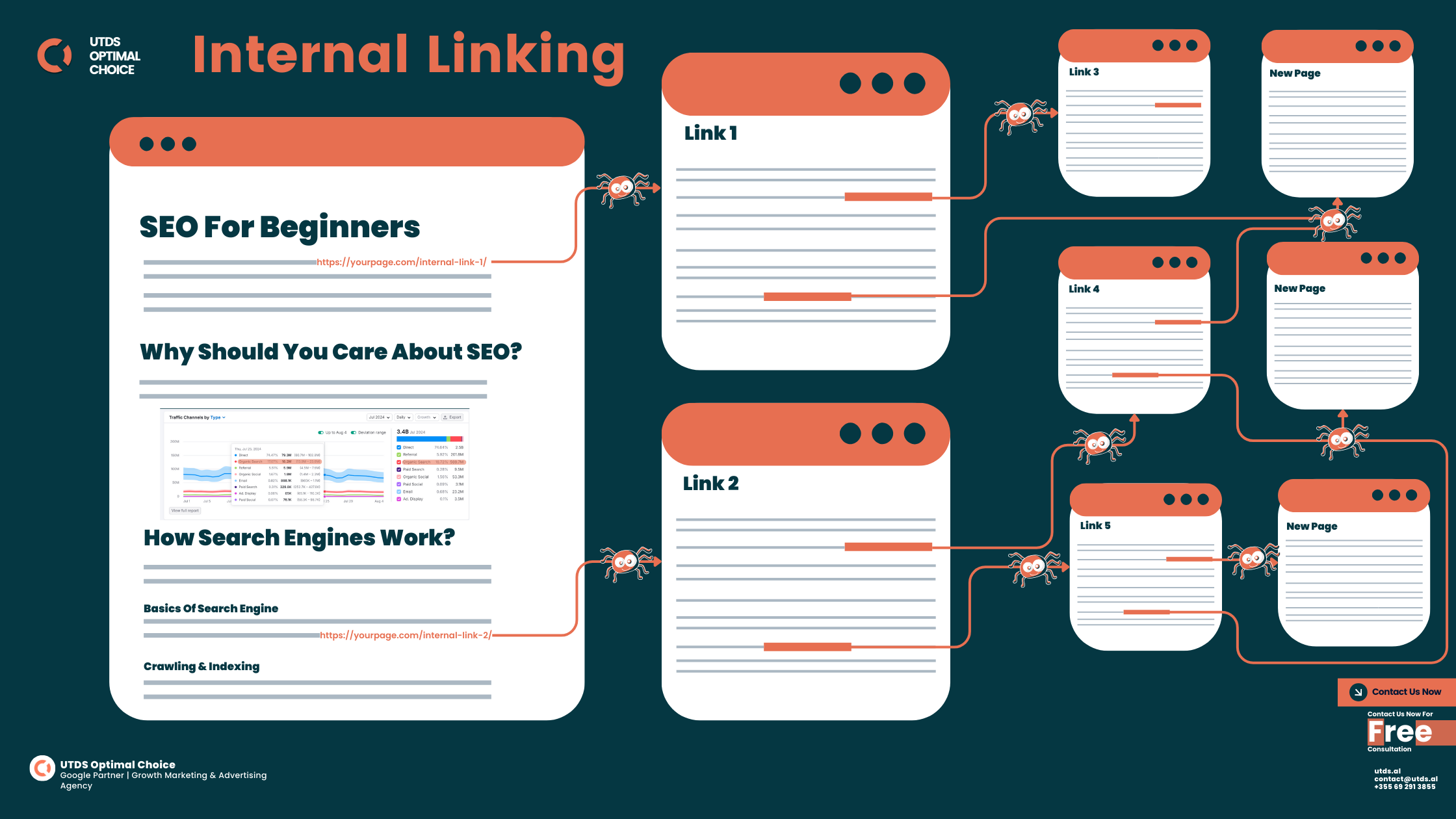
Internal linking is a powerful but often overlooked aspect of SEO. It helps search engines understand your site structure and spreads link equity throughout your site. Here’s how to do it effectively:
Why Internal Linking Matters
- Helps search engines discover and index your pages
- Distributes page authority throughout your site
- Improves user navigation and keeps visitors on your site longer
Create a Strong Site Structure
- Organise your content into clear categories
- Use a logical hierarchy (Home > Category > Subcategory > Individual Page)
- Aim for a flat structure where most pages are within 3-4 clicks from the homepage
Use Descriptive Anchor Text
- The clickable text in a link should describe the linked page
- Include relevant keywords, but keep it natural
- Avoid generic phrases like “click here” or “read more“
- Example: “Learn more about choosing the right running shoes for your foot type“
Link from High-Authority Pages
- Your homepage and main category pages typically have the most authority
- Link from these pages to important deeper pages to pass on that authority
Use Contextual Links
- Place links within your content where they’re most relevant
- This provides context for both users and search engines
- Link to Related Content
- At the end of blog posts, include links to related articles
- In product descriptions, link to related products or buying guides
Update Old Content with New Links
- Regularly revisit older content to add links to newer, related pages
- This keeps your old content fresh and helps your new content get discovered
Use a Reasonable Number of Links
- There’s no strict limit, but aim for quality over quantity
- A good rule of thumb is to include minimum 5 internal links per 1000 words of content
Consider Using a Related Posts Plugin
- For blogs, this can automatically suggest related content to readers
Create Topic Clusters
- Group related content around a central “pillar” page
- Link from the pillar page to more specific related pages, and vice versa
Use Your Navigation Wisely
- Include links to your most important pages in your main navigation
- Consider using a footer menu for additional important links
The goal of internal linking is to provide value to your users while helping search engines understand your site structure. Always prioritise creating a logical, easy-to-navigate site over trying to manipulate search rankings.
Ready to optimise your website's content for better rankings? At UTDS Optimal Choice, we specialise in On page Optimisation that improves your site’s visibility and user experience. From meta tags to internal linking, we’ll help you fine-tune every element to boost your search performance. Get in touch today, and let us help you unlock the full potential of your website with expert on-page SEO strategies!
Technical SEO
Site Speed Optimisation
Site speed isn’t just about user experience—it’s a crucial factor for SEO. Here’s why speed matters and how to improve it:
Why Speed Matters
- User Experience: Visitors leave slow sites, increasing bounce rates.
- Mobile Performance: Speed is even more critical on mobile devices.
- Search Rankings: Google considers site speed in its ranking algorithms.
How to Check Your Site Speed
Use Google PageSpeed Insights (https://pagespeed.web.dev/):
- Enter your URL and click “Analyse“
- Review your scores for both mobile and desktop
- Check the “Opportunities” and “Diagnostics” sections for specific improvements
Tips to Improve Site Speed
- Optimise Images
- Compress images using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim
- Use modern formats like WebP for better compression
- Implement lazy loading for images below the fold
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
- Remove unnecessary characters and spaces from your code
- Use tools like Minifier or plugins for your CMS
- Leverage Browser Caching
- Set expiration dates for certain file types
- This tells browsers to load previously downloaded resources from local disk rather than over the network
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- CDNs distribute your content across multiple, geographically diverse servers
- This reduces distance between users and your website’s server
- Enable Compression
- Use Gzip compression to reduce the size of your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files
- Reduce Server Response Time
- Optimise your server configuration
- Consider upgrading your hosting plan or switching to a faster provider
Improving site speed is an ongoing process. Regularly test your site and make improvements to ensure it stays fast as you add new content and features.
Mobile Optimisation
With more than half of web traffic coming from mobile friendly websites, mobile optimisation is no longer optional—it’s essential. Here’s how to ensure your site is mobile-friendly:
Why Mobile Optimisation Matters
- Mobile First Indexing: Google primarily uses the mobile version of content for ranking and indexing.
- User Experience: Mobile users have different needs and behaviours compared to desktop users.
- Local SEO: Many local searches happen on mobile devices.
Key Elements of Mobile Optimisation
- Responsive Design
- Your site should automatically adjust to fit different screen sizes
- Use flexible layouts, images, and cascading style sheet (CSS) media queries
- Touch-Friendly Navigation
- Use large, easy-to-tap buttons
- Implement a clear menu structure, consider a hamburger menu for mobile
- Fast Loading Times
- Mobile users often have slower connections, so speed is crucial
- Implement the speed optimisation techniques mentioned earlier
- Readable Text Without Zooming
- Use a font size of at least 14px for body text
- Ensure adequate contrast between text and background
- Avoid Flash and Pop-ups
- Flash isn’t supported on most mobile devices
- Pop-ups can be particularly disruptive on small screens
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
AMP is an open-source framework designed to create fast-loading mobile web pages.
- Pros: Very fast loading, potential for improved visibility in search results
- Cons: Limited functionality, can be complex to implement
How to Test Mobile-Friendliness
- Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test:
- Visit https://search.google.com/test/mobile-friendly
- Enter your URL and get a report on mobile-friendliness
- Chrome DevTools:
- Open your site in Chrome
- Right-click and select “Inspect“
- Click the “Toggle device toolbar” icon to simulate different mobile devices
- Real Device Testing:
- Test your site on various physical mobile devices
- Pay attention to loading times, navigation, and overall user experience
As new devices and technologies emerge, continue to test and refine your mobile experience.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)

SSL certificates are no longer just for e-commerce sites—they’re a must-have for any website. Here’s why SSL matters and how to implement it:
Why SSL is Important
- Security: SSL encrypts data transferred between users and your site, protecting sensitive information.
- Trust: Users see a padlock icon in their browser, indicating a secure connection.
- SEO Boost: Google gives a ranking boost to HTTPS sites.
How SSL Works
- SSL creates an encrypted connection between a user’s browser and your server.
- This is indicated by “https://” at the start of your URL, instead of “http://“.
Implementing SSL
- Choose an SSL Certificate:
- Free options: Let’s Encrypt, Cloudflare
- Paid options: Offer additional features and sometimes stronger encryption
- Install the Certificate:
- If you’re using a hosting provider, they often offer one-click SSL installation
- For self-hosted sites, you’ll need to install the certificate on your server
- Update Your Site to Use HTTPS:
- Change internal links to HTTPS
- Update any hard coded links to resources (images, scripts, etc.)
- Set Up 301 Redirects:
- Redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS
- Update External Links:
- If possible, update links from other sites to use HTTPS
- Update Your Google Search Console and Analytics:
- Add the HTTPS version of your site as a new property
Remember to renew your SSL certificate before it expires to maintain continuous protection and avoid security warnings for your users.
XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt
XML sitemaps and robots.txt files are like roadmaps and traffic signs for search engines. Here’s how to use them effectively:
XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the important pages on your website, helping search engines find and index your content.
Creating an XML Sitemap:
- Use a Sitemap Generator:
- If you’re using WordPress, plugins like Yoast SEO can create sitemaps automatically
- For other platforms, try online tools like XML-Sitemaps.com
- Structure Your Sitemap:
- Include all important pages
- Use priority tags to indicate the relative importance of pages
- Use changefreq tags to show how often pages are updated
- Keep It Updated:
- Generate a new sitemap whenever you add or remove pages
- Many CMS plugins can do this automatically
Submitting Your Sitemap:
- Add your sitemap URL to your robots.txt file:
Sitemap: https://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml - Submit directly to search engines:
- Google: Submit through Google Search Console
- Bing: Submit through Bing Webmaster Tools
Robots.txt
A robots.txt file tells search engines which parts of your site they should and shouldn’t crawl. [So when should you use a robot.txt file?]
Creating a Robots.txt File:
- Create a text file named “robots.txt”
- Place it in your root directory (e.g., www.yourwebsite.com/robots.txt)
Example Robots.txt Content:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /private/
Disallow: /tmp/
Allow: /
This example allows all robots to crawl your site, except for the /private/ and /tmp/ directories.
Sitemap: https://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
Best Practices:
- Don’t use robots.txt to hide sensitive information (use password protection instead)
- Test your robots.txt file using the robots.txt Tester in Google Search Console
- Be careful not to accidentally block important content
Robots.txt can suggest which areas to avoid, it’s not a security measure. For sensitive content, use more robust methods like password protection or noindex tags.
Off-Page SEO and Link Building
What is Off-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO refers to all the actions you take outside of your own website to improve its search engine rankings. While on page SEO focuses on optimising your content and site structure, off-page SEO is all about building your site’s authority and credibility in the eyes of search engines and users.
Key components of off-page SEO include:
- Backlinks: Links from other websites to yours.
- Social signals: Shares, likes, and overall social media visibility.
- Brand mentions: References to your brand, even without a link.
- Local SEO: Managing your Google My Business listing and local citations.
The primary goal of off-page SEO is to show search engines that your website is valuable, credible, and relevant. When other reputable sites link to or mention yours, it’s like a vote of confidence. The more high-quality “votes” you have, the more likely search engines are to rank your site higher for relevant queries.
Remember, off-page SEO is not about gaming the system. It’s about creating genuine value and building real relationships. By focusing on off-page SEO, you’re not just improving your search rankings – you’re building your brand’s online presence and authority in your industry. [Here is how to set up Google My Business Profile]
Importance of Backlinks
Backlinks, also known as inbound links or incoming links, are links from other websites that point to your site. They’re like the currency of the internet – the more high quality backlinks you have, the richer your site is in the eyes of search engines. Here’s why they’re so crucial:
Why Backlinks Matter
- Authority Signal: Backlinks are like endorsements. When a reputable site links to yours, it’s telling search engines, “This site is trustworthy and has valuable content.“
- Discoverability: Backlinks help search engines discover new pages on your site. The more backlinks you have, the more often search engines will crawl and index your content.
- Referral Traffic: Good backlinks don’t just improve SEO – they can also drive direct website traffic to your site from people clicking on the links.
- Brand Exposure: Even if people don’t click, seeing your brand mentioned on other sites increases awareness and credibility.
What Makes a High-Quality Backlink
Not all backlinks are created equal. Here’s what makes a backlink valuable:
- Relevance: The linking site should be topically related to yours. A link from a cooking blog to a mechanic’s website isn’t as valuable as one from an auto parts supplier.
- Authority: Links from well-established, respected sites carry more weight. Tools like Moz’s Domain Authority can help you assess a site’s authority.
- Placement: A link within the main content of a page is typically more valuable than one in the footer or sidebar.
- Anchor Text: The clickable text of the link should be relevant to your page’s content. However, be careful not to over-optimise – too many exact-match anchor texts can look suspicious.
- Dofollow vs. Nofollow: “Dofollow” links pass SEO value, while “nofollow” links typically don’t. However, a mix of both looks more natural.
- Uniqueness: Getting links from a variety of different domains is better than multiple links from the same domain.
Impact of Backlinks on SEO
Backlinks play a crucial role in how search engines rank your site:
- Ranking Factor: Backlinks are one of Google’s top three ranking factors, alongside content and RankBrain (Google’s AI system).
- Page Authority: Pages with more high-quality backlinks typically rank higher for their target keywords.
- Domain Authority: Sites with strong backlink profiles often have better overall visibility in search results.
- Topic Relevance: Backlinks help search engines understand what topics your site is authoritative about.
A few links from highly respected, relevant sites can be more valuable than hundreds of low-quality links. Focus on earning backlinks naturally through great content and relationship building, rather than trying to game the system with artificial link schemes.
How to Build Quality Backlinks

Building a strong backlink profile is crucial for SEO success, but it requires time, effort, and a strategic approach. Here are some effective strategies to earn high-quality backlinks:
1. Create Link-Worthy Content
The foundation of any successful link-building strategy is outstanding content. People naturally link to content that is:
- Informative and in-depth
- Unique or innovative
- Visual (infographics, videos, interactive tools)
- Backed by original research or data
Note: Develop a content calendar focused on creating comprehensive, value-packed content in your niche.
2. Guest Posting
Writing articles for other reputable websites in your industry can earn you quality backlinks and increase your brand exposure.
How to do it right:
- Target sites relevant to your industry
- Pitch unique, valuable content ideas
- Follow the site’s guest posting guidelines
- Include a natural link back to your site in the content or author bio
Note: Make a list of 10 relevant blogs in your industry and start building relationships with their editors.
3. Broken Link Building
This involves finding broken links on other websites and suggesting your content as a replacement.
Steps:
- Find relevant pages with lots of outbound links
- Use a tool like Check My Links to identify broken links
- Create or find content on your site that could replace the broken link
- Reach out to the site owner, informing them about the broken link and suggesting your content as a replacement
Note: Install the Check My Links extension and start looking for opportunities on industry-related sites.
4. Skyscraper Technique
This involves:
- Finding popular content in your niche
- Creating something even better
- Reaching out to sites linking to the original content and suggesting your improved version
Note: Use a tool like Ahrefs to find a popular piece of content in your niche and brainstorm ways to dramatically improve it.
5. Resource Page Link Building
Many websites have resource pages that link to useful content. Find these pages and suggest your content for inclusion.
Note: Search for “[your topic] + resource page” and make a list of relevant opportunities.
6. PR and Relationship Building
Building relationships with journalists, bloggers, and influencers in your industry can lead to natural link opportunities.
Tactics:
- Engage with influencers on social media
- Offer expert quotes or interviews
- Sponsor or speak at industry events
Note: Follow 5 key influencers in your industry on social media and start meaningfully engaging with their content.
7. Create Linkable Assets
Develop resources that people in your industry would naturally want to link to, such as:
- Free tools or calculators
- Industry surveys or original research
- Comprehensive guides or whitepapers
Note: Brainstorm a useful tool or resource you could create for your audience.
Avoiding Black-Hat SEO Techniques
While building links, it’s crucial to avoid practices that could result in penalties:
- Don’t buy links: Purchasing links violates Google’s guidelines and can result in severe penalties.
- Avoid link farms: These are networks of low-quality sites created solely for link building.
- Say no to automated link building: Mass-producing low-quality links through automated tools is a recipe for disaster.
- Don’t engage in link exchanges: Excessive reciprocal linking can look unnatural.
The goal is to earn links naturally by providing value. It takes time and effort, but the results are worth it. Focus on creating great content and building genuine relationships in your industry. Over time, you’ll develop a strong, natural backlink profile that boosts your SEO and establishes your site as an authority in your field.
Looking to boost your website’s authority and climb the search rankings? At UTDS Optimal Choice, we focus on off-page SEO strategies to enhance your online presence. Our team can help you drive traffic and improve your site's credibility. Contact us today and start strengthening your off-page SEO to outrank the competition!
Measuring and Analysing SEO Success
Key SEO Metrics to Track
To effectively manage your SEO efforts, you need to focus on the right metrics. Here are the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will give you a comprehensive view of your SEO success:
Organic Traffic
- The number of visitors coming to your site from organic search results.
- This is a direct indicator of your SEO effectiveness. Increasing organic traffic suggests your SEO efforts are paying off.
Keyword Rankings
- The position of your website in search results for specific keywords.
- Higher rankings lead to more visibility and clicks.
Bounce Rate
- The percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page.
- A high bounce rate might indicate that your content isn’t meeting user expectations or that you’re targeting the wrong keywords.
Conversion Rate
- The percentage of visitors who complete a desired action (e.g., making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter).
- This shows how well your SEO efforts are contributing to your business goals.
Page Load Time
- How long it takes for your pages to fully load.
- Faster sites tend to rank better and provide a better user experience. [Here is how website speed impacts SEO]
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- The percentage of people who click on your site in search results.
- A higher CTR indicates that your title tags and meta descriptions are effective.
Backlink Profile
- The quantity and quality of links pointing to your site.
- Backlinks are a crucial ranking factor and indicate your site’s authority.
Organic Visibility
- The overall visibility of your site in search results across a set of keywords.
- This gives you a broader view of your SEO performance beyond individual keyword rankings.
These metrics should not be viewed in isolation. They work together to give you a complete picture of your SEO performance. Regularly monitoring these KPIs will help you identify trends, spot issues early, and measure the impact of your SEO efforts.
Using Google Analytics and Search Console

Google Analytics and Google Search Console are powerful, free tools that provide invaluable insights into your website’s performance. Here’s how to set them up and use them effectively for SEO:
Setting Up Google Analytics
- Create a Google Analytics Account
- Go to analytics.google.com and sign up
- Click “Start measuring“
- Follow the prompts to set up your account, property, and data stream
- Install the Tracking Code
- In your Google Analytics property, go to Admin > Property > Data Streams
- Select your stream and find the Measurement ID
- Copy the provided Global Site Tag (gtag.js) code
- Paste this code into the <head> section of every page on your site
- Set Up Goals
- In Google Analytics, go to Admin > View > Goals
- Click “New Goal” and follow the prompts to set up conversions you want to track.
- [ Here is the complete Google Analytics help guide to help you get started]
Setting Up Google Search Console
- Add Your Property
- Go to search.google.com/search-console
- Click “Add property“
- Choose your preferred verification method (Domain or URL prefix)
- Verify Ownership
- Follow the instructions for your chosen verification method
- Common methods include uploading an HTML file or adding a meta tag to your site’s home page
- Submit Your Sitemap
- In Search Console, go to Sitemaps
- Enter the URL of your sitemap and click “Submit“
- [ Here is the complete Google Search Console help guide to help you get started]
Using Google Analytics for SEO
- Analyse Organic Traffic
- Go to Acquisition > All Traffic > Channels
- Click on “Organic Search” to see details about your organic visitors
- Identify Top-Performing Content
- Go to Behaviour > Site Content > All Pages
- Sort by organic traffic to see which pages attract the most search visitors
- Monitor Site Speed
- Go to Behaviour > Site Speed > Page Timings
- Identify pages that need speed optimisation
Using Google Search Console for SEO
- Monitor Keyword Performance
- Go to Performance > Search Results > Queries
- See which keywords are driving traffic to your site
- Analyse Click-Through Rates
- In the Performance report, look at the CTR column
- Identify opportunities to improve your meta titles and descriptions
- Check for Indexing Issues
- Go to Indexing > Pages
- Address any errors or warnings to ensure all your pages are being indexed
- Monitor Backlinks
- Go to Links > External links
- See which sites are linking to you and what your most linked content is
By regularly using these tools, you’ll gain valuable insights into your SEO performance and be able to make data-driven decisions to improve your strategy.
How Can We Help You?
At UTDS Optimal Choice, we specialise in optimising your website to achieve top rankings on search engines. From keyword research to on-page, off-page, and technical SEO, we tailor strategies that align with your business goals. Our focus is on driving long-term success with transparent reporting and continuous support. We ensure your website attracts the right audience and stays ahead of the competition.
We are a data-driven, client-focused SEO agency committed to ethical, white-hat practices. We use cutting-edge techniques to deliver measurable results. We prioritise transparency, keeping you informed at every step, and adapt strategies as the digital landscape evolves. Ready to grow your business with us? Contact us today to get started!